Overview of Previous Research
Reconstruction And Analysis Of Historical Social Networks
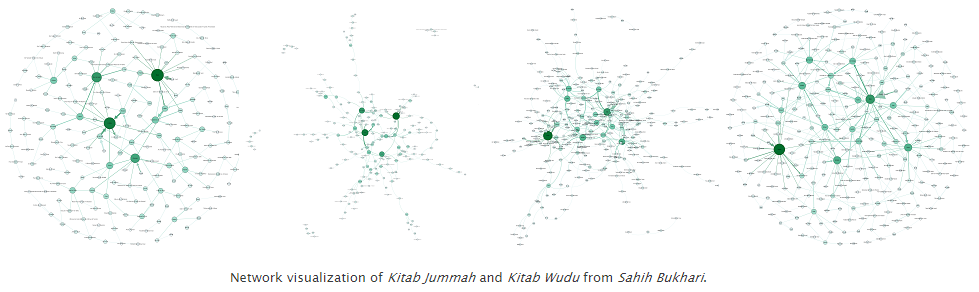 Historical documents offer a wealth of information about the past including social linkages between people. The aim of this project is to use ancient and medieval texts in various languages to reconstruct social networks. Using medieval and early modern texts in Arabic and English we have been able to reconstruct a social network of more than 20,000 people spanning the globe and all the major civilizations of the world.
Historical documents offer a wealth of information about the past including social linkages between people. The aim of this project is to use ancient and medieval texts in various languages to reconstruct social networks. Using medieval and early modern texts in Arabic and English we have been able to reconstruct a social network of more than 20,000 people spanning the globe and all the major civilizations of the world.
- Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad Towards the Analysis of Narrative Networks Technical Report 13-017 Department of Computer Science University of Minnesota May 23, 2013
- Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad Information Network Analysis meets Islamic Studies: Case study from the Analysis of the Hadith Literature Society for the Scientific Study of Religion Annual Conference. Boston, MA November 7, 2013
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb. “Towards the Analysis of Narrative Networks.” Tech. Rep. number13-017, Department of Computer Science and Engineering …, 2013.Details
Personality Emulation Of The Deceased
The death of my father had a profound effect on me. It made me realize that my children will never have the opportunity to interact with him. This has prompted me to start work on this project where the aim is to create simulations of deceased people so that the living can interact with them. In this project not only are the requirements for creating such a system explored but their implications at the intersection of artificial intelligence, natural language processing, psychology and sociology.
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb. “After Death: Big Data and the Promise of Resurrection by Proxy.” In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 397–408, 2016.Details
Data Mining Pilgrimage Data
Every year millions of Muslims go to the Holy cities of Mecca and Medina to perform the pilgrimage of Hajj. Over the course of just two weeks more than 3 million people are housed within an area less the size of Manhattan. Routing and providing services such a large mass of people is a logistical challenge that can be addressed via the application of machine learning to Big Data. This project was focused on data mining pilgrimage data in order to provide provide insights that can greatly improve the logistics of Hajj.
Modeling Human Behavior In Massive Online Games
This work was done as part of the Virtual Worlds Observatory project which was a multi-disciplinary collaboration between University of Minnesota, University of Southern California, University of Illinois – Urbana Champaign and Northwestern University. This project was focused on the use of machine learning to model human behavior in massive online games to study phenomenon like team formation, trust formation and evolution, predictive models for demographic characteristics (age, gender etc.) and behavioral characteristics (leadership, political affiliation, deviancy etc).
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, and Jaideep Srivastava. “Behavioral Data Mining and Network Analysis in Massive Online Games.” In Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, 673–74, 2014.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Cuihua Shen, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “On the Problem of Predicting Real World Characteristics from Virtual Worlds.” In Predicting Real World Behaviors from Virtual World Data, 1–18. Springer, 2014.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Cuihua Shen, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir . Contractor. Predicting Real World Behaviors from Virtual World Data. Springer, 2014.Details
- Borbora, Zoheb Hassan, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Jehwan Oh, Karen Zita Haigh, Jaideep Srivastava, and Zhen Wen. “Robust Features of Trust in Social Networks.” Social Network Analysis and Mining 3, no. 4 (2013): 981–99.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Brian Keegan, Atanu Roy, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Guilt by Association? Network Based Propagation Approaches for Gold Farmer Detection.” In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, 121–26, 2013.Details
- Williams, Dmitri, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Jaideep Srivastava, Brian Keegan, and Noshir Contractor. “Automatic Detection of Deviant Players in Massively Multiplayer Online Role Playing Games (Mmogs).” Google Patents, 2013.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Zoheb Borbora, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Love All, Trust a Few: Link Prediction for Trust and Psycho-Social Factors in MMOs.” In International Conference on Social Computing, Behavioral-Cultural Modeling, and Prediction, 123–30. Springer, 2012.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb. “Computational Trust in Multiplayer Online Games.,” 2012.Details
- Roy, Atanu, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Chandrima Sarkar, Brian Keegan, and Jaideep Srivastava. “The Ones That Got Away: False Negative Estimation Based Approaches for Gold Farmer Detection.” In 2012 International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2012 International Confernece on Social Computing, 328–37. IEEE, 2012.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Iftekhar Ahmed, Jaideep Srivastava, and Marshall Scott Poole. “Trust Me, i’m an Expert: Trust, Homophily and Expertise in Mmos.” In 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Social Computing, 882–87. IEEE, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Brian Keegan, Sophia Sullivan, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Illicit Bits: Detecting and Analyzing Contraband Networks in Massively Multiplayer Online Games.” In 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Social Computing, 127–34. IEEE, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Zoheb Borbora, Cuihua Shen, Jaideep Srivastava, and Dmitri Williams. “Guild Play in MMOGs: Rethinking Common Group Dynamics Models.” In International Conference on Social Informatics, 145–52. Springer, 2011.Details
- Borbora, Zoheb H, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Karen Zita Haigh, Jaideep Srivastava, and Zhen Wen. “Exploration of Robust Features of Trust across Multiple Social Networks.” In 2011 Fifth IEEE Conference on Self-Adaptive and Self-Organizing Systems Workshops, 27–32. IEEE, 2011.Details
- Wang, Jing, David A Huffaker, Jeffrey W Treem, Lindsay Fullerton, Muhammad A Ahmad, Dmitri Williams, Marshall Scott Poole, and Noshir Contractor. “Focused on the Prize: Characteristics of Experts in Massive Multiplayer Online Games.” First Monday, 2011.Details
- Keegan, Brian, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “What Can Gold Farmers Teach Us about Criminal Networks?” XRDS: Crossroads, The ACM Magazine for Students 17, no. 3 (2011): 11–15.Details
- Shim, Kyong Jin, Nishith Pathak, Muhammad A Ahmad, Colin DeLong, Zoheb Borbora, Amogh Mahapatra, and Jaideep Srivastava. “Analyzing Human Behavior from Multiplayer Online Game Logs: A Knowledge Discovery Approach.” IEEE Intelligent Systems 26, no. 1 (2011): 85–89.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, and J Srivastava. “Item Recommendations in Multiple Overlapping Social Networks in MMOs.” In The Third ACM WebSci Conference, Koblenz, Germany June, 14–17, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, and Jaideep Srivastava. “Models of Social Capital for Predicting Success in MMOs.” In The Third ACM WebSci Conference, Koblenz, Germany June, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, and J Srivastava. “Models of Social Capital for Predicting Success in MMOs.” In The Third ACM WebSci Conference, Koblenz, Germany June, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, David Huffaker, Jing Wang, Jeff Treem, Dinesh Kumar, Marshall Scott Poole, and Jaideep Srivastava. “The Many Faces of Mentoring in an Mmorpg.” In 2010 IEEE Second International Conference on Social Computing, 270–75. IEEE, 2010.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Marshall Scott Poole, and Jaideep Srivastava. “Network Exchange in Trust Networks.” In 2010 IEEE Second International Conference on Social Computing, 341–46. IEEE, 2010.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, David Huffakar, Jing Wang, Jeff Treem, Marshall Scott Poole, and Jaideep Srivastava. “GTPA: A Generative Model for Online Mentor-Apprentice Networks.” In Twenty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2010.Details
- Keegan, Brian, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmed, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Dark Gold: Statistical Properties of Clandestine Networks in Massively Multiplayer Online Games.” In 2010 IEEE Second International Conference on Social Computing, 201–8. IEEE, 2010.Details
- Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Brian Keegan, Jaideep Srivastava, Dmitri Williams, and Noshir Contractor. “Mining for Gold Farmers: Automatic Detection of Deviant Players in Mmogs.” In 2009 International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, 4:340–45. IEEE, 2009.Details
- Shim, Kyong Jin, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Nishith Pathak, and Jaideep Srivastava. “Inferring Player Rating from Performance Data in Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (MMORPGs).” In 2009 International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, 4:1199–1204. IEEE, 2009.Details
- Xiong, Li, Marshall Scott Poole, Dmitri Williams, and Muhammad A Ahmad. “The Effects of Group Structure on Group Outcomes in an Online Game,” 2006.Details
Computational Models Of Trust In Massive Online Games
Computational trust refers to the mediation of trust via a computational infrastructure. In this project questions related to trust in complex social environments represented by Massively Multiplayer Online Games (MMOGs) are explored. The main emphasis is that trust is a multi-level phenomenon both in terms of how it operates at multiple levels of network granularities and how trust relates to other social phenomenon like homophily, expertise, mentoring, clandestine behaviors etc. Social contexts and social environments affect not just the qualitative aspects of trust but this phenomenon is also manifested with respect to the network and structural signatures of trust network.
Clandestine And Deviant Behaviors In Massive Online Games
Gold Farming refers to a set of inter-related activities in online virtual spaces especially in Massively Multiplayer Games where certain players engage in repetitive activities to gain virtual commodities which they sell to other players. Game administrators actively ban Gold Farmers who have to hide their activities from the game admins, who are akin to law enforcers. In our research we compared Gold Farmers with their offline criminal counterparts. It was discovered that the behaviors of Gold Farmers is very similar to real world criminals in that their social networks tend to be quite similar.
- Williams, Dmitri, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Jaideep Srivastava, Brian Keegan, and Noshir Contractor. “Automatic Detection of Deviant Players in Massively Multiplayer Online Role Playing Games (Mmogs).” Google Patents, 2013.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Brian Keegan, Atanu Roy, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Guilt by Association? Network Based Propagation Approaches for Gold Farmer Detection.” In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, 121–26, 2013.Details
- Roy, Atanu, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Chandrima Sarkar, Brian Keegan, and Jaideep Srivastava. “The Ones That Got Away: False Negative Estimation Based Approaches for Gold Farmer Detection.” In 2012 International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2012 International Confernece on Social Computing, 328–37. IEEE, 2012.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Brian Keegan, Sophia Sullivan, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Illicit Bits: Detecting and Analyzing Contraband Networks in Massively Multiplayer Online Games.” In 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Privacy, Security, Risk and Trust and 2011 IEEE Third International Conference on Social Computing, 127–34. IEEE, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Brian Keegan, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir S Contractor. “Trust Amongst Rogues? A Hypergraph Approach for Comparing Clandestine Trust Networks in MMOGs.” In ICWSM, 2011.Details
- Keegan, Brian, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir S Contractor. “Sic Transit Gloria Mundi Virtuali? Promise and Peril in the Computational Social Science of Clandestine Organizing.” Proceedings of the 3rd International Web Science Conference, 2011.Details
- Keegan, Brian, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “What Can Gold Farmers Teach Us about Criminal Networks?” XRDS: Crossroads, The ACM Magazine for Students 17, no. 3 (2011): 11–15.Details
- Keegan, Brian, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmed, Dmitri Williams, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Dark Gold: Statistical Properties of Clandestine Networks in Massively Multiplayer Online Games.” In 2010 IEEE Second International Conference on Social Computing, 201–8. IEEE, 2010.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Brian Keegan, Jaideep Srivastava, Dmitri Williams, and Noshir Contractor. “Mining for Gold Farmers: Automatic Detection of Deviant Players in Mmogs.” In 2009 International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering, 4:340–45. IEEE, 2009.Details
Link Prediction
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Zoheb Borbora, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Love All, Trust a Few: Link Prediction for Trust and Psycho-Social Factors in MMOs.” In International Conference on Social Computing, Behavioral-Cultural Modeling, and Prediction, 123–30. Springer, 2012.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, and J Srivastava. “Item Recommendations in Multiple Overlapping Social Networks in MMOs.” In The Third ACM WebSci Conference, Koblenz, Germany June, 14–17, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Marshall Scott Poole, and J Srivastava. “ The Trust Propensity Prediction Problem.” In The Third ACM WebSci Conference, Koblenz, Germany June, 2011.Details
- Borbora, Zoheb H, Muhammad Aurangzeb Ahmad, Karen Zita Haigh, Jaideep Srivastava, and Zhen Wen. “Exploration of Robust Features of Trust across Multiple Social Networks.” In 2011 Fifth IEEE Conference on Self-Adaptive and Self-Organizing Systems Workshops, 27–32. IEEE, 2011.Details
- Ahmad, Muhammad Aurangzeb, Zoheb Borbora, Jaideep Srivastava, and Noshir Contractor. “Link Prediction across Multiple Social Networks.” In 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, 911–18. IEEE, 2010.Details
Machine Learning For Historical Census Data
Before the US instituted Social Security numbers as a way to uniquely identify all US citizens, there was no way to identify people across US censuses. The aim of this project was to develop a machine learning model and framework to link people across US historical census data from 1850 to 1910 e.g., linking and then tracking the same person from 1850, 1860, 1870, 1880, 1900 to 1910 censuses.
Data Mining ICD Data
The aim of this project is to extract useful insights from ICD (Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator). This is the project that I did at Boston Scientific in St. Paul Minnesota. Time series data for tachycardia/tachyarrhythmia and other types of arrhythmia was extracted and different pattern set mining techniques were applied to it. This project hit close to home later on because my father was implanted with the device that I worked on.
